We all want our website to be at the top of search results. It’s as obvious as wanting a sunny day for a beach trip. But how do you get a higher search engine ranking?
That’s the million-dollar question.
One that we’ll answer in this article; with practical and actionable steps that can take your site from the shadows to the spotlight.
Get comfortable, here’s how to rank higher on Google.
On-page SEO optimization
The first step to ranking higher is optimizing your website itself. This is on-page SEO and it involves adjusting your content and structure to signal to search engines that your site is relevant and valuable to users.
Some important ways to optimize your website pages include:
1. Keyword research and integration
Find specific phrases and questions that your users type into search engines.
- In Google Keyword Planner
- Click Discover new keywords
- Enter the products or services you offer
- Enter your website in the input field below it
- You can tweak your language or location
- Click Get results
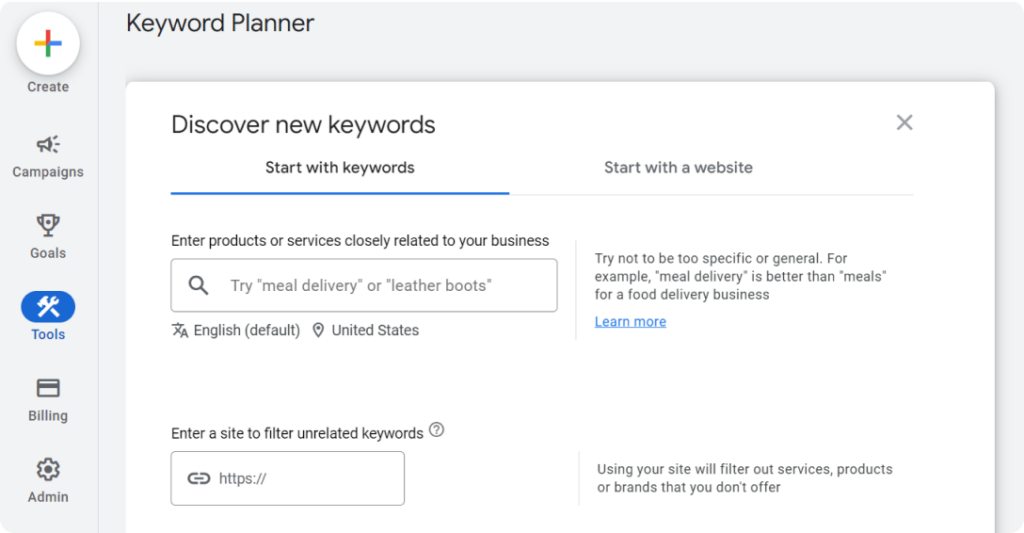
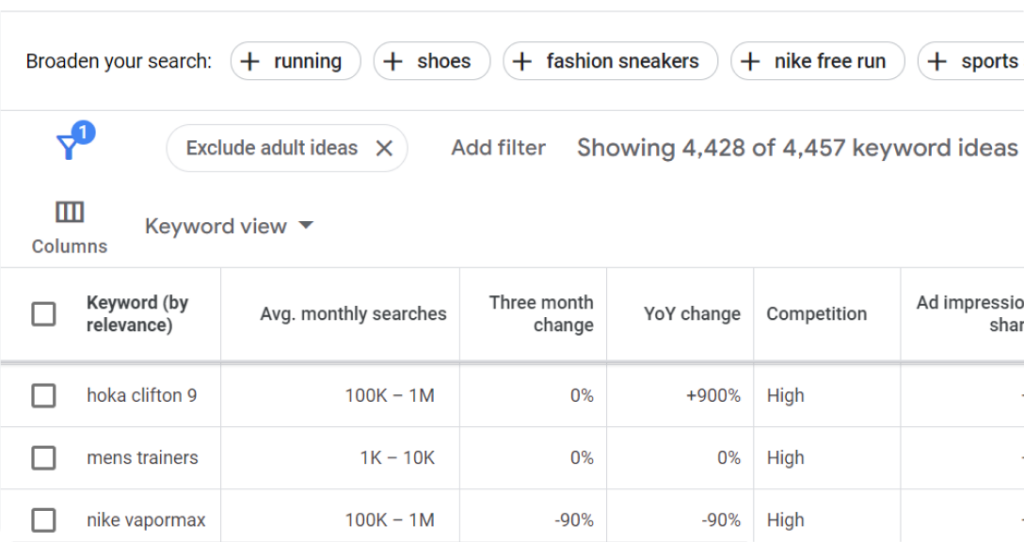
Exclude brands/products you do not offer, filter your results, and select keywords with high search volume but lower competition.
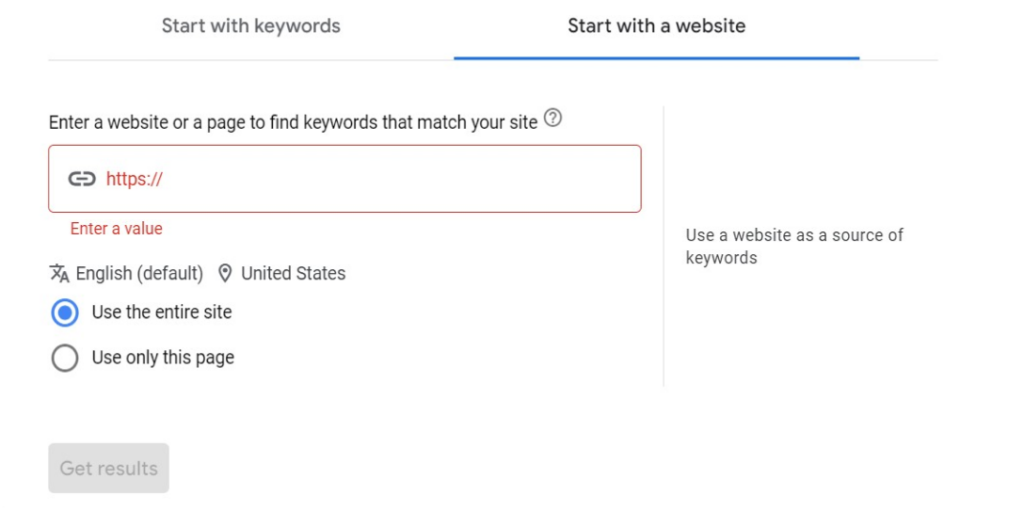
If you’re interested in your competitors’ keywords—and you should be—use the “Start with a website” feature instead.
Pro tip: Don’t focus on single-word “head terms” with high competition. Pick long-tail keywords too. These are more specific phrases users add to their search.
For instance, instead of just “running shoes,” a long-tail keyword could be “best lightweight running shoes for women.” These keywords often have lower competition and higher conversion rates since people who search for them are further along the buyer journey.
2. Target topic clusters
Structure your content around topic clusters. These are groups of interlinked pages that comprehensively address a central theme.
You can actively target topic clusters by weaving in Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) keywords throughout your content.
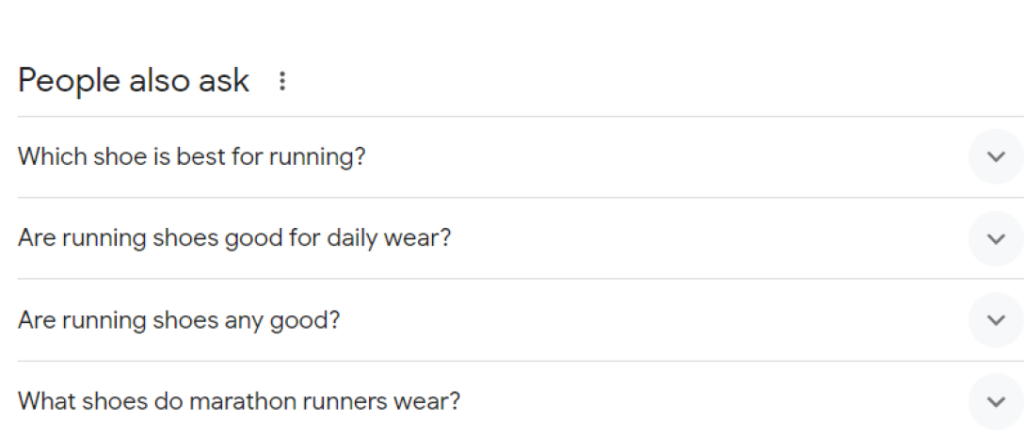
A good way to find low-hanging topic clusters is through the “People also ask” section on Google search.
3. Match user intent
Create articles that align with your users’ search goals.
For instance, a Google search for “best running shoes” shows that most websites focus on educational content and product comparisons—not a sales pitch for their brands ❌.
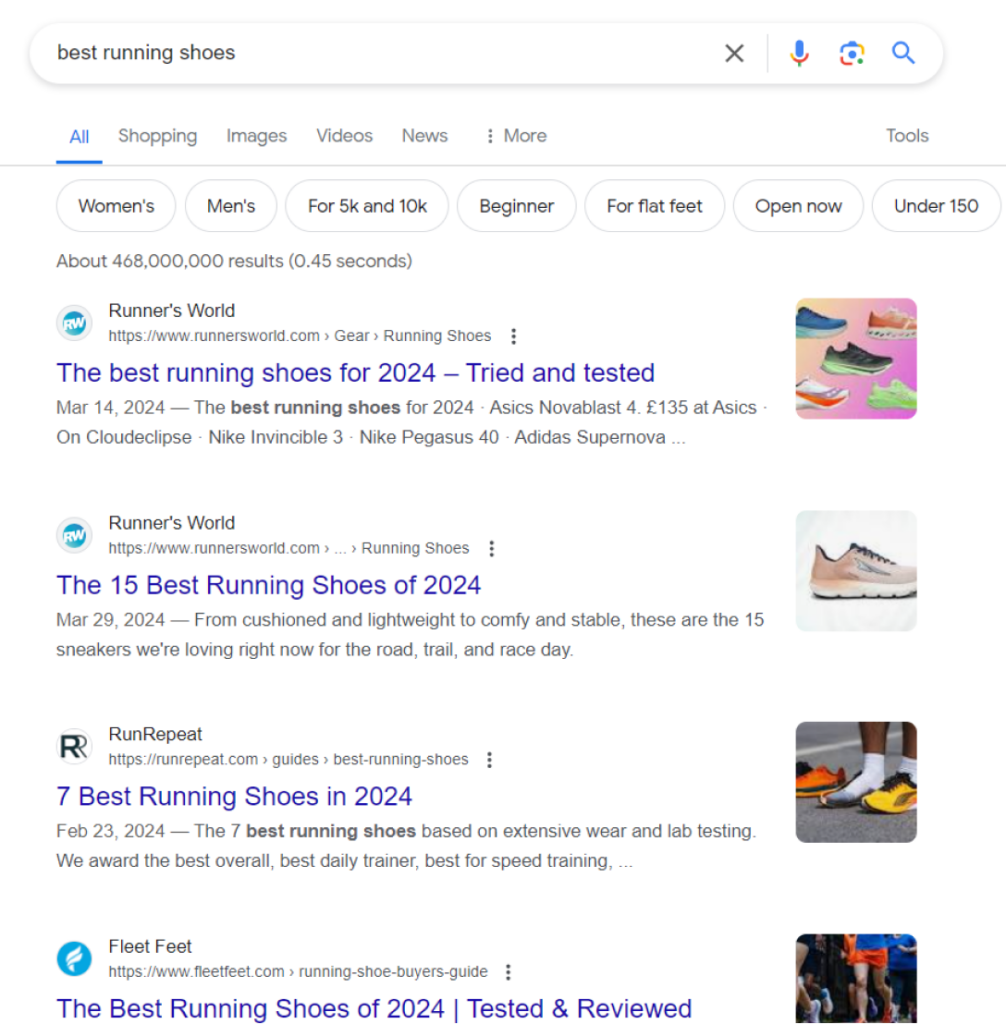
You should do the same. However, you can differentiate by providing evergreen content like “Best Running Shoes for Beginners.”
Bottomline is, if people cannot find what they need quickly, Google will assume your site is not useful, so it’ll be demoted.
4. Add internal links
Internal linking involves connecting relevant pages on your website with hyperlinks.
For instance, on your product page for “running shoes,” you could link to a blog post titled “Choosing the Right Running Shoes for Your Needs.”
You can find your internal links through a site search (site:domain.com “[keyword]”)
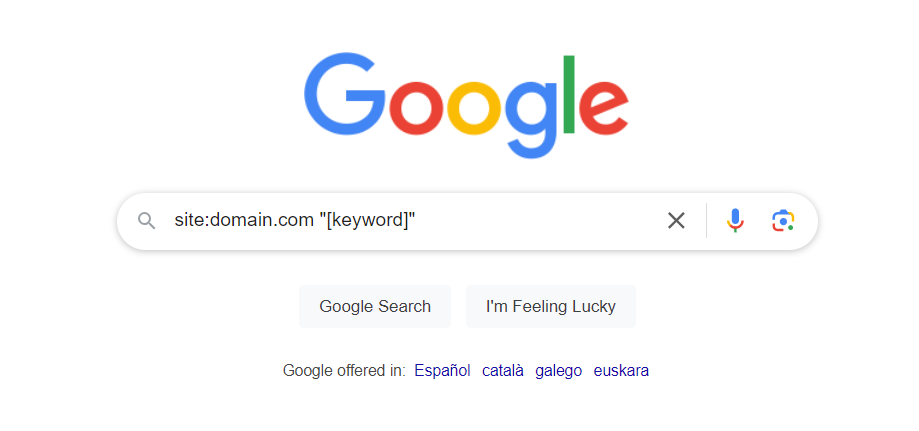
Internal linking helps users discover deeper content, improves website navigation, and distributes “link juice” (ranking power) throughout your site.
5. Optimize images
High-quality, relevant images engage the reader, yes. But, they also contribute to a high search engine ranking.
Here’s how to optimize them:
- Make them meaningful (infographics, workflow screenshots, charts, etc)
- Optimize image sizes for faster loading times.
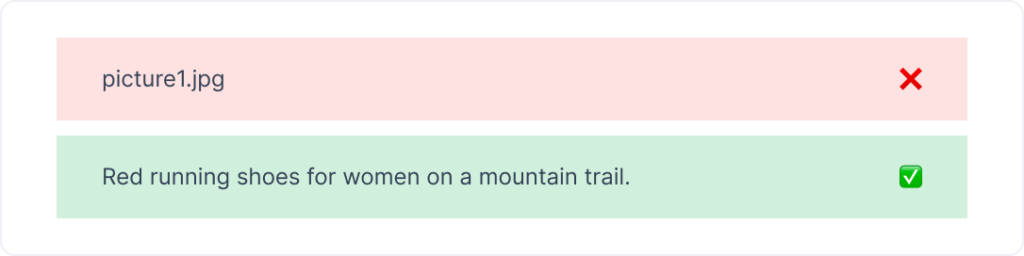
- Add descriptive alt text and relevant keywords. This helps search engines understand the image content and improves accessibility for visually impaired users.
6. Provide helpful content
The heart of on-page SEO lies in offering content that’s genuinely valuable to your users. We’ve covered a bit of this in User Intent, but to be more specific, your content should follow Google’s E-A-T principles.
No, they’re not burgers. It stands for:
- Expertise
- Authoritativeness
- Trustworthiness

Pro tip: Remember to regularly update your website with fresh content to keep users engaged and signal to search engines that your site is active and relevant.
Technical SEO considerations
Technical SEO involves optimizing the technical aspects of a website to help search engines crawl, index, and understand your site. Some often overlooked aspects of technical SEO include:
- Site speed: Fast-loading pages provide a better user experience.
- Mobile responsiveness: All elements of your site should load accurately on mobile.
Pro tip: You can test site speed and mobile-responsiveness with Google’s PageSpeed Insights.
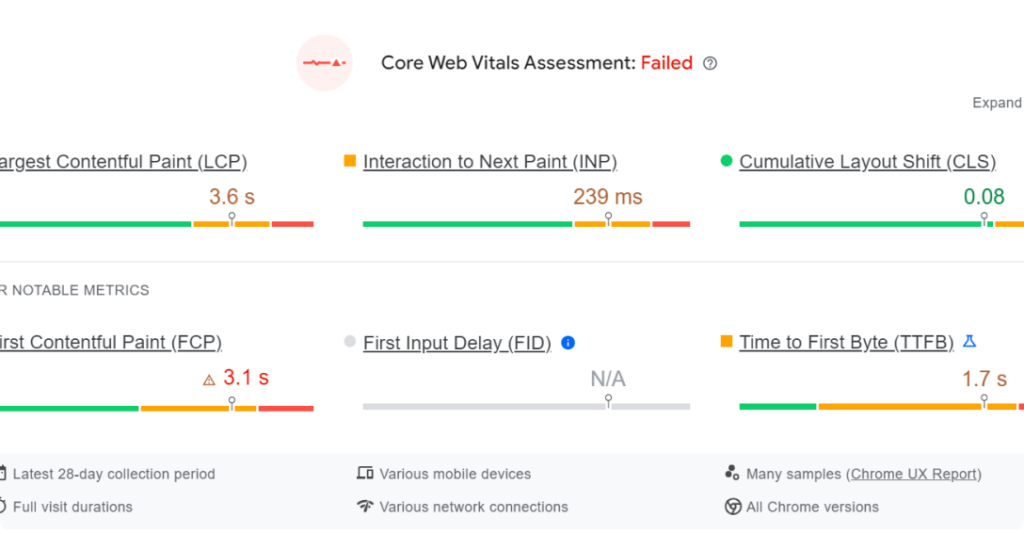
Source: Google
- Secure sockets layer (SSL): Site security contributes to your page experience, which is an important ranking signal for Google. So, be sure to use an SSL to secure your site.
- Duplicate content: Avoid duplicate content issues by setting up canonical URLs and using the `rel=canonical` tag properly.
Off-page SEO strategies
Off-page SEO are activities outside your website that influence its search engine ranking and credibility. It’s primarily focused on building the authority of your website through links, social media, and mentions from other sites—backlinks.
How to build backlinks
The more high-quality websites linking to you, the more authority you gain in Google’s eyes. Some ways to build strong backlinks include:
Broken link building
- How to do it: Find relevant websites with broken or outdated links on topics related to yours. You can search for a website’s deadlinks with Deadlinkchecker.
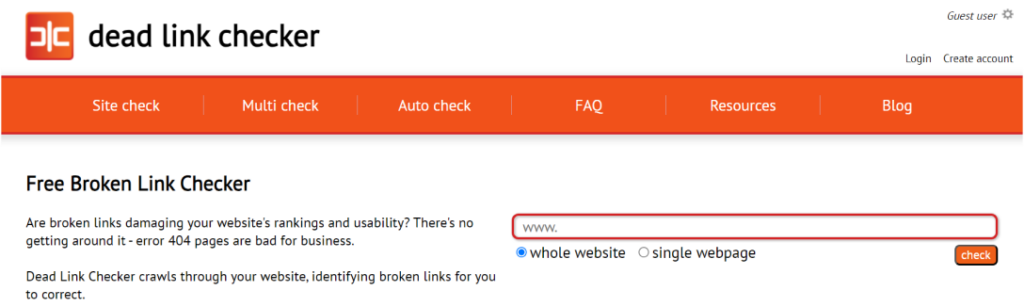
- Action: Contact the website owner and suggest your high-quality content as a replacement in exchange for a backlink.
Guest blogging
- How to do it: Identify high-authority blogs in your niche that accept guest posts.
- Action: Pitch them a well-written and informative guest post idea that aligns with their audience’s interests.
Brand building & online reputation management
- How to do it: Submit your websites to trusted platforms like Google My Business, G2, or Yelp.
- Action: Encourage customer reviews on those platforms and on social. Respond to both positive and negative reviews professionally.
Multilingual SEO for international businesses
Regular SEO focuses on optimizing your website for search engines in one language. While this is important, international businesses have the potential to reach a much wider audience by implementing multilingual SEO.
And here’s how to do so.
- Conduct language-specific keyword research: Remember that direct keyword translation may not capture the right intent.
- Choose a good website structure: Decide on a structure (country-code top-level domain, subdomain, or subdirectory) for each language version of your site.
- Make locally relevant content: Localize content beyond translation by considering cultural context and regional trends.
- Add hreflang tags: Implement hreflang tags to specify the language and geographical targeting of a webpage
- Implement local link building: Get links from websites in the target language region to improve local search relevance.
- Optimize metadata: Translate page titles, meta descriptions, and alt text for images.
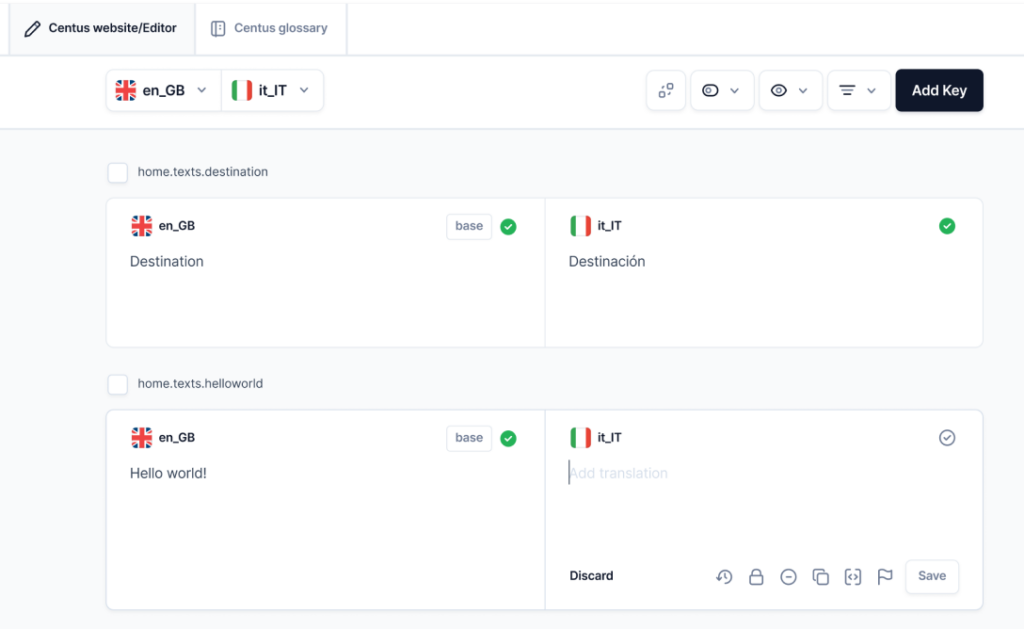
Juggling all these elements and their translations is difficult, especially when done in a rush. Consider using a website localization platform to streamline the process and ensure consistency across all languages. It’s also important to build your multilingual SEO strategy while you’re developing your local website.
Pro tip: You can simplify your multilingual SEO process with a translation management tool that doubles as a project manager. It’ll do all the checks, manage your translations, and keep you on track.
Parting thoughts
We’ve explored various strategies to help you improve your website’s Google ranking. They can be summed up in 4 simple sentences.
- Create high-quality, informative content that answers your target audience’s search intent.
- Ensure your website is mobile-friendly, loads quickly, and has the appropriate keywords.
- Build backlinks from reputable websites to your content and establish your website’s authority in your niche.
- Prepare for multilingual SEO if you want to expand to other markets.
Remember, SEO is not stagnant. Track your website’s performance using analytics tools and see what’s working and what’s not. Don’t be afraid to experiment with different tactics and see what drives the most traffic.
Comments 0
No comments yet. Start the conversation!





